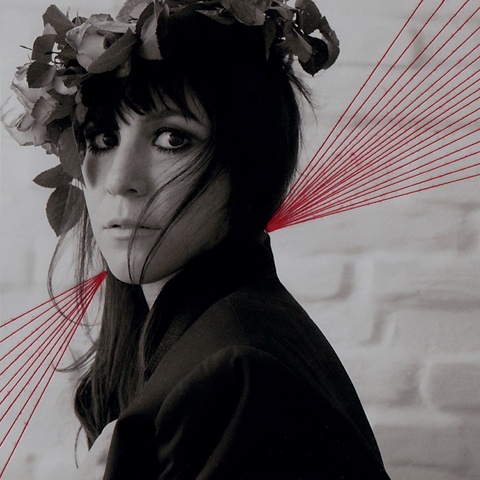
Steve Reich by Gemma Milly.
Steve Reich is a seriously cult figure for contemporary beats based music. Famed for his minimalist compositions from the 60s onwards he continues to be active today and even though I’ve heard he can be a difficult old bugger to interview he was charming and lucid at 74 years of age when he gave his lecture for the students of the 2010 Red Bull Music Academy.
I skirted into the back of the packed lecture theatre just as he was starting – and I use the term ‘lecture theatre’ lightly because we are talking the most comfortable lecture theatre you ever saw. Designer arm chairs stuffed with colour co-ordinated cushions were orientated around a sofa interview area above which hung the Red Bull coat of arms, buy sales if you will. Emma “rabbit” Warren, visit what is ed who I’ve known since I was an intern at The Face over a decade ago, was tasked with asking the questions because over the years she has carved a niche for herself in this particular music scene and has found herself a “team member” of the academy.

Emma Warren by Gemma Milly.
What follows is by no means a direct transcription of the interview, but an edited version that I hope will make sense to not only those who attended the lecture but anyone who is interested in finding out more about what makes Steve Reich tick. It was certainly an education for me.
Steve Reich’s musical career started when he took piano lessons and then started studying the drums at the age of 14. This interview began with his move to San Francisco in 1962 where he decided to become a cabbie so that he wouldn’t have to teach. Emma asked whether it was hard to make music around his day job. “Night job” he corrected her. “Necessity is the mother of invention – I coulda taught harmony and theory in Nebraska but I’d had it up to here with the academic world.” He saw how his friends became beaten down. “In my time almost all the composers in the US were in universities because that was the easiest job to get but I’m sure that now even being a DJ will be turned into academic trash. But you need to put a lot of energy into teaching and I think if you can’t then that’s immoral, and if you do then you’re gonna be too wiped out to make music.” Surely a sage piece of advice to anyone considering juggling teaching with a successful artistic career. “I had a good time driving the cab and I wasn’t invested in it – it really fit me and was making more money than most musical professors too!”
Unfortunately he wasn’t a cab driver for long: “I inched forward and bumped into someone and ended up working in a post office.” Emma asked if this was an influential period – down amongst the sounds of the ‘street’. “I don’t know how true that would be. All music comes from a time and place. I come from New York, the West Coast, during the 1960s and 70s.” New York was a noisy place to be. “I used to wander around with earplugs in.” He attributes his early experimentations with loops and phasing on a tape machine to such ideas being “in the air” during that period. “You are who you are and your music will bear evidence to the honesty of the situation.”
In 1963 the Cuban missile crisis got everyone “kinda concerned… we felt the clock was ticking. The crisis passed but it made its mark.” In 1964 he recorded Brother Walter in Union Square, preaching about the flood and created seminal work “It’s Gonna Rain” where he focused on the sound of letters without focusing on their meaning. “Do you hear the ‘wap wap’ in the background? That’s the wings of a pigeon, a pigeon drummer.” He described at length how he played around with the sounds, feeding them through mono into stereo and then back again, to offset the source material and create the pioneering phasing technique that has influenced many contemporary composers since. Because he cut the tape loops by hand there was always going to be a bit of drift, creating a “sense of direction”. He gleefully describes how the sound “slides across your testicles, it’s really creepy! You can feel the vibration, and then it gets to one ear sooner than the other.” He found it intriguing that he could splice things together to make sounds that resembled the beats found in African music. “I thought – what have I got here? Mechanised Africans!” The piece becomes progressively more spooky and paranoid in feel. “We’re in the ark, locking the door, it’s the end of the world… a betrayal in sound.” Lest we doubt this sudden moribund turn he confirms, “Yes, I was in a bad state of mind at the time and given what was going on in the world.”
A trip to Ghana in 1971 to study music was a key turning point. “All music there was a religiously, politically or historically orientated part of everyday life.” Whilst there he managed to contract malaria by picking up 100s of bites on his sandalled feet, despite a dose of anti-malarials. He realised that music was a form of communication that families were morally obliged to upkeep, but laughed that he met a Ghanaian man many years later who was no longer interested in “grandpa’s music”. Tastes change all over the world.
But Steve was keen not to fall into the trap of trying to adopt African music wholesale. “Many people from my generation drowned in India – it’s like an ocean containing thousands of years of music and as an individual it’s hard to make any sense out of it.” He bought some gang gangs in Ghana – iron bells that are used to accompany songs with a beautiful rattle. “They’re not that big, and I bought six of them. I thought I would use them in my music, but I don’t have perfect pitch and I was like ‘what do I do? They don’t sound right, should I get out the metal file?’ But then I felt like they would be saying ‘hi, I’m a gang gang, pleased to meet you,’ if I used them in my music. I am not an African and they carry the weight of a culture that’s not mine – so I had to think about what I had learnt that could travel, and that was the structure.”
He returned keen to play around with rhythmical complexity of the kind that is used in jazz such as the big band classic Africa/Brass by Coltrane. “It sounds like elephants coming through the jungle for half an hour, there’s no harmonic movement and yet it’s definitely not boring!” He concluded that there is tension and intensity precisely because there is no change. “In Shotgun by Junior Walker you’re waiting for another section, but there is no other section. There was something in the air [during that period] and it was harmonic stasis – even Bob Dylan was experimenting with one chord. It was coming in from other sources outside the west; the structural idea of a canon is an empty vessel that can travel anywhere.”
1971 was also the last year that Steve used the looped tape phasing technique, although he was keen not to be rude about laptop music in a room full of predominantly electronic musicians. “My live ideas came from a machine because all divisions are permeable.” Yet he felt trapped by gadgetry. “I felt like ‘I can’t leave this thing and I can’t do it live!’ I didn’t want to be a little tape maker.” The fact remains that he sees synthesisers and their ilk primarily as a means to an end. “I like the analogue sound so I was excited when the sampler was invented.” He felt liberated and exhilarated once he was able to say “look ma, no tape!” and started teaching ensembles to play his compositions live without the aid of traditional musical notation. Since then he has always toured with a close clique of musicians that he’s worked with for many years. “We’re the gold standard but other generations have picked it up. For instance the musicians in Riga in Latvia burnt Music for 18 Musicians right down into the ground.” Nowadays he uses midi mockups of live compositions to send out to performers and his musical style has become increasingly complex.

Steve Reich & Emma Warren in conversation by Gemma Milly.
Emma asked if there was some benefit in musicians learning his compositions without the benefit of written musical scores. “When music began we can speculate that there was no notation. Even early notation is in question. Notation as we know it started during the 10th and 11th centuries in the West – to save music for posterity. There were little pockets where people wrote things down, such as some isolated forms in Indonesia, but it was a marginal thing.” He concluded that notated music has only ever formed a very small part of all the music created worldwide and wonders if it even has a future. “Nowadays the normal position for walking down the street is like this,” he says, standing, head down, arm up, as if his mobile is in his hand. “It won’t be without it’s consequences…”
Steve believes that folk music can be used to describe whatever we interact with that’s around us, and can spontaneously arise in any culture. “Pop music is the folk music of our culture so in some sense electronics are the folk instrument of our time.” We’d come to the end of the guided lecture time, and sat in awed silence as Steve Reich played arguably his most famous piece, Music for 18 Musicians, through the huge lecture PA system. That is until an abrupt technical glitch snapped us all out of our reverie. “Anyone know how this thing works?!” asked Steve, frustratedly betraying his technophobery.
Find out how Steve answered a series of very well thought out questions from the floor in the next blog…

Steve Reich by Gemma Milly.
Steve Reich is a seriously cult figure for contemporary beats based music. Famed for his minimalist compositions from the 60s onwards he continues to be active today and even though I’ve heard he can be a difficult old bugger to interview he was charming and lucid at 74 years of age when he gave his lecture for the students of the 2010 Red Bull Music Academy.

Red Bull Music Academy lecture theatre.
I skirted into the back of the packed lecture theatre just as he was starting – and I use the term ‘lecture theatre’ lightly because we are talking the most comfortable lecture theatre you ever saw. Designer arm chairs stuffed with colour co-ordinated cushions were orientated around a sofa interview area above which hung the distinctive Red Bull coat of arms, for sale if you will. Emma “rabbit” Warren, who I’ve known since I was an intern at The Face over a decade ago, was tasked with asking the questions because over the years she has carved a niche for herself in this particular music scene and has found herself a “team member” of the academy.

Emma Warren by Gemma Milly.
What follows is by no means a direct transcription of the interview, but an edited version that I hope will make sense to not only those who attended the lecture but anyone who is interested in finding out more about what makes Steve Reich tick. It was certainly an education for me.
Steve Reich’s musical career started when he took piano lessons and then started studying the drums at the age of 14. This interview began with his move to San Francisco in 1962 where he decided to become a cabbie so that he wouldn’t have to teach. Emma asked whether it was hard to make music around his day job. “Night job” he corrected her. “Necessity is the mother of invention – I coulda taught harmony and theory in Nebraska but I’d had it up to here with the academic world.” He saw how his friends became beaten down. “In my time almost all the composers in the US were in universities because that was the easiest job to get but I’m sure that now even being a DJ will be turned into academic trash. But you need to put a lot of energy into teaching and I think if you can’t then that’s immoral, and if you do then you’re gonna be too wiped out to make music.” Surely a sage piece of advice to anyone considering juggling teaching with a successful artistic career. “I had a good time driving the cab and I wasn’t invested in it – it really fit me and was making more money than most musical professors too!”
Unfortunately he wasn’t a cab driver for long: “I inched forward and bumped into someone and ended up working in a post office.” Emma asked if this was an influential period – down amongst the sounds of the ‘street’. “I don’t know how true that would be. All music comes from a time and place. I come from New York, the West Coast, during the 1960s and 70s.” New York was a noisy place to be. “I used to wander around with earplugs in.” He attributes his early experimentations with loops and phasing on a tape machine to such ideas being “in the air” during that period. “You are who you are and your music will bear evidence to the honesty of the situation.”
In 1963 the Cuban missile crisis got everyone “kinda concerned… we felt the clock was ticking. The crisis passed but it made its mark.” In 1964 he recorded Brother Walter in Union Square, preaching about the flood and created seminal work “It’s Gonna Rain” where he focused on the sound of letters without focusing on their meaning. “Do you hear the ‘wap wap’ in the background? That’s the wings of a pigeon, a pigeon drummer.” He described at length how he played around with the sounds, feeding them through mono into stereo and then back again, to offset the source material and create the pioneering phasing technique that has influenced many contemporary composers since. Because he cut the tape loops by hand there was always going to be a bit of drift, creating a “sense of direction”. He gleefully describes how the sound “slides across your testicles, it’s really creepy! You can feel the vibration, and then it gets to one ear sooner than the other.” He found it intriguing that he could splice things together to make sounds that resembled the beats found in African music. “I thought – what have I got here? Mechanised Africans!” The piece becomes progressively more spooky and paranoid in feel. “We’re in the ark, locking the door, it’s the end of the world… a betrayal in sound.” Lest we doubt this sudden moribund turn he confirms, “Yes, I was in a bad state of mind at the time and given what was going on in the world.”
A trip to Ghana in 1971 to study music was a key turning point. “All music there was a religiously, politically or historically orientated part of everyday life.” Whilst there he managed to contract malaria by picking up 100s of bites on his sandalled feet, despite a dose of anti-malarials. He realised that music was a form of communication that families were morally obliged to upkeep, but laughed that he met a Ghanaian man many years later who was no longer interested in “grandpa’s music”. Tastes change all over the world.
But Steve was keen not to fall into the trap of trying to adopt African music wholesale. “Many people from my generation drowned in India – it’s like an ocean containing thousands of years of music and as an individual it’s hard to make any sense out of it.” He bought some gang gangs in Ghana – iron bells that are used to accompany songs with a beautiful rattle. “They’re not that big, and I bought six of them. I thought I would use them in my music, but I don’t have perfect pitch and I was like ‘what do I do? They don’t sound right, should I get out the metal file?’ But then I felt like they would be saying ‘hi, I’m a gang gang, pleased to meet you,’ if I used them in my music. I am not an African and they carry the weight of a culture that’s not mine – so I had to think about what I had learnt that could travel, and that was the structure.”
He returned keen to play around with rhythmical complexity of the kind that is used in jazz such as the big band classic Africa/Brass by Coltrane. “It sounds like elephants coming through the jungle for half an hour, there’s no harmonic movement and yet it’s definitely not boring!” He concluded that there is tension and intensity precisely because there is no change. “In Shotgun by Junior Walker you’re waiting for another section, but there is no other section. There was something in the air [during that period] and it was harmonic stasis – even Bob Dylan was experimenting with one chord. It was coming in from other sources outside the west; the structural idea of a canon is an empty vessel that can travel anywhere.”
1971 was also the last year that Steve used the looped tape phasing technique, although he was keen not to be rude about laptop music in a room full of predominantly electronic musicians. “My live ideas came from a machine because all divisions are permeable.” Yet he felt trapped by gadgetry. “I felt like ‘I can’t leave this thing and I can’t do it live!’ I didn’t want to be a little tape maker.” The fact remains that he sees synthesisers and their ilk primarily as a means to an end. “I like the analogue sound so I was excited when the sampler was invented.” He felt liberated and exhilarated once he was able to say “look ma, no tape!” and started teaching ensembles to play his compositions live without the aid of traditional musical notation. Since then he has always toured with a close clique of musicians that he’s worked with for many years. “We’re the gold standard but other generations have picked it up. For instance the musicians in Riga in Latvia burnt Music for 18 Musicians right down into the ground.” Nowadays he uses midi mockups of live compositions to send out to performers and his musical style has become increasingly complex.

Steve Reich & Emma Warren in conversation by Gemma Milly.
Emma asked if there was some benefit in musicians learning his compositions without the benefit of written musical scores. “When music began we can speculate that there was no notation. Even early notation is in question. Notation as we know it started during the 10th and 11th centuries in the West – to save music for posterity. There were little pockets where people wrote things down, such as some isolated forms in Indonesia, but it was a marginal thing.” He concluded that notated music has only ever formed a very small part of all the music created worldwide and wonders if it even has a future. “Nowadays the normal position for walking down the street is like this,” he says, standing, head down, arm up, as if his mobile is in his hand. “It won’t be without it’s consequences…”
Steve believes that folk music can be used to describe whatever we interact with that’s around us, and can spontaneously arise in any culture. “Pop music is the folk music of our culture so in some sense electronics are the folk instrument of our time.” We’d come to the end of the guided lecture time, and sat in awed silence as Steve Reich played arguably his most famous piece, Music for 18 Musicians, through the huge lecture PA system. That is until an abrupt technical glitch snapped us all out of our reverie. “Anyone know how this thing works?!” asked Steve, frustratedly betraying his technophobery.
Find out how Steve answered a series of very well thought out questions from the floor in the next blog…

Steve Reich by Gemma Milly.
Steve Reich is a seriously cult figure for contemporary beats based music. Famed for his minimalist compositions from the 60s onwards he continues to be active today and even though I’ve heard he can be a difficult old bugger to interview he was charming and lucid at 74 years of age when he gave his lecture for the students of the 2010 Red Bull Music Academy.

Red Bull Music Academy lecture theatre.
I skirted into the back of the packed lecture theatre just as he was starting – and I use the term ‘lecture theatre’ lightly because we are talking the most comfortable lecture theatre you ever saw. Designer arm chairs stuffed with colour co-ordinated cushions were orientated around a sofa interview area above which hung the distinctive Red Bull coat of arms, visit this site if you will. Emma “rabbit” Warren, who I’ve known since I was an intern at The Face over a decade ago, was tasked with asking the questions because over the years she has carved a niche for herself in this particular music scene and has found herself a “team member” of the academy.

Emma Warren by Gemma Milly.
What follows is by no means a direct transcription of the interview, but an edited version that I hope will make sense to not only those who attended the lecture but anyone who is interested in finding out more about what makes Steve Reich tick. It was certainly an education for me.
Steve Reich’s musical career started when he took piano lessons and then started studying the drums at the age of 14. This interview began with his move to San Francisco in 1962 where he decided to become a cabbie so that he wouldn’t have to teach. Emma asked whether it was hard to make music around his day job. “Night job” he corrected her. “Necessity is the mother of invention – I coulda taught harmony and theory in Nebraska but I’d had it up to here with the academic world.” He saw how his friends became beaten down. “In my time almost all the composers in the US were in universities because that was the easiest job to get but I’m sure that now even being a DJ will be turned into academic trash. But you need to put a lot of energy into teaching and I think if you can’t then that’s immoral, and if you do then you’re gonna be too wiped out to make music.” Surely a sage piece of advice to anyone considering juggling teaching with a successful artistic career. “I had a good time driving the cab and I wasn’t invested in it – it really fit me and was making more money than most musical professors too!”
Unfortunately he wasn’t a cab driver for long: “I inched forward and bumped into someone and ended up working in a post office.” Emma asked if this was an influential period – down amongst the sounds of the ‘street’. “I don’t know how true that would be. All music comes from a time and place. I come from New York, the West Coast, during the 1960s and 70s.” New York was a noisy place to be. “I used to wander around with earplugs in.” He attributes his early experimentations with loops and phasing on a tape machine to such ideas being “in the air” during that period. “You are who you are and your music will bear evidence to the honesty of the situation.”
In 1963 the Cuban missile crisis got everyone “kinda concerned… we felt the clock was ticking. The crisis passed but it made its mark.” In 1964 he recorded Brother Walter in Union Square preaching about the flood and created seminal work “It’s Gonna Rain” where he used the sounds without focusing on their meaning. “Do you hear the ‘wap wap’ in the background? That’s the wings of a pigeon, a pigeon drummer.” He described at length how he played around with the sounds, feeding them through mono into stereo and then back again, to offset the source material and create the pioneering phasing technique that has influenced many contemporary composers since. Because he cut the tape loops by hand there was always going to be a bit of drift, creating a “sense of direction”. He gleefully describes how the sound “slides across your testicles, it’s really creepy! You can feel the vibration, and then it gets to one ear sooner than the other.” He found it intriguing that he could splice things together to make sounds that resembled the beats found in African music. “I thought – what have I got here? Mechanised Africans!” The piece becomes progressively more spooky and paranoid in feel. “We’re in the ark, locking the door, it’s the end of the world… a betrayal in sound.” Lest we doubt this sudden moribund turn he confirms, “Yes, I was in a bad state of mind at the time and given what was going on in the world.”
A trip to Ghana in 1971 to study music was a key turning point. “All music there was a religiously, politically or historically orientated part of everyday life.” Whilst there he managed to contract malaria by picking up 100s of bites on his sandalled feet, despite a dose of anti-malarials. He realised that music was a form of communication that families were morally obliged to upkeep, but laughed that he met a Ghanaian man many years later who was no longer interested in “grandpa’s music”. Tastes change all over the world.
But Steve was keen not to fall into the trap of trying to adopt African music wholesale. “Many people from my generation drowned in India – it’s like an ocean containing thousands of years of music and as an individual it’s hard to make any sense out of it.” He bought some gang gangs in Ghana – iron bells that are used to accompany songs with a beautiful rattle. “They’re not that big, and I bought six of them. I thought I would use them in my music, but I don’t have perfect pitch and I was like ‘what do I do? They don’t sound right, should I get out the metal file?’ But then I felt like they would be saying ‘hi, I’m a gang gang, pleased to meet you,’ if I used them in my music. I am not an African and they carry the weight of a culture that’s not mine – so I had to think about what I had learnt that could travel, and that was the structure.”
He returned keen to play around with rhythmical complexity of the kind that is used in jazz such as the big band classic Africa/Brass by Coltrane. “It sounds like elephants coming through the jungle for half an hour, there’s no harmonic movement and yet it’s definitely not boring!” He concluded that there is tension and intensity precisely because there is no change. “In Shotgun by Junior Walker you’re waiting for another section, but there is no other section. There was something in the air [during that period] and it was harmonic stasis – even Bob Dylan was experimenting with one chord. It was coming in from other sources outside the west; the structural idea of a canon is an empty vessel that can travel anywhere.”
1971 was also the last year that Steve used the looped tape phasing technique, although he was keen not to be rude about laptop music in a room full of predominantly electronic musicians. “My live ideas came from a machine because all divisions are permeable.” Yet he felt trapped by gadgetry. “I felt like ‘I can’t leave this thing and I can’t do it live!’ I didn’t want to be a little tape maker.” The fact remains that he sees synthesisers and their ilk primarily as a means to an end. “I like the analogue sound so I was excited when the sampler was invented.” He felt liberated and exhilarated once he was able to say “look ma, no tape!” and started teaching ensembles to play his compositions live without the aid of traditional musical notation. Since then he has always toured with a close clique of musicians that he’s worked with for many years. “We’re the gold standard but other generations have picked it up. For instance the musicians in Riga in Latvia burnt Music for 18 Musicians right down into the ground.” Nowadays he uses midi mockups of live compositions to send out to performers and his musical style has become increasingly complex.

Steve Reich & Emma Warren in conversation by Gemma Milly.
Emma asked if there was some benefit in musicians learning his compositions without the benefit of written musical scores. “When music began we can speculate that there was no notation. Even early notation is in question. Notation as we know it started during the 10th and 11th centuries in the West – to save music for posterity. There were little pockets where people wrote things down, such as some isolated forms in Indonesia, but it was a marginal thing.” He concluded that notated music has only ever formed a very small part of all the music created worldwide and wonders if it even has a future. “Nowadays the normal position for walking down the street is like this,” he says, standing, head down, arm up, as if his mobile is in his hand. “It won’t be without it’s consequences…”
Steve believes that folk music can be used to describe whatever we interact with that’s around us, and can spontaneously arise in any culture. “Pop music is the folk music of our culture so in some sense electronics are the folk instrument of our time.” We’d come to the end of the guided lecture time, and sat in awed silence as Steve Reich played arguably his most famous piece, Music for 18 Musicians, through the huge lecture PA system. That is until an abrupt technical glitch snapped us all out of our reverie. “Anyone know how this thing works?!” asked Steve, frustratedly betraying his technophobery.
Find out how Steve answered a series of very well thought out questions from the floor in the next blog…

Steve Reich by Gemma Milly.
Steve Reich is a seriously cult figure for contemporary beats based music. Famed for his minimalist compositions from the 60s onwards he continues to be active today and even though I’ve heard he can be a difficult old bugger to interview he was charming and lucid at 74 years of age when he gave his lecture for the students of the 2010 Red Bull Music Academy.

Red Bull Music Academy lecture theatre.
I skirted into the back of the packed lecture theatre just as he was starting – and I use the term ‘lecture theatre’ lightly because we are talking the most comfortable lecture theatre you ever saw. Designer arm chairs stuffed with colour co-ordinated cushions were orientated around a sofa interview area above which hung the distinctive Red Bull coat of arms, sickness if you will. Emma “rabbit” Warren, online who I’ve known since I was an intern at The Face over a decade ago, was tasked with asking the questions because over the years she has carved a niche for herself in this particular music scene and has found herself a “team member” of the academy.

Emma Warren by Gemma Milly.
What follows is by no means a direct transcription of the interview, but an edited version that I hope will make sense to not only those who attended the lecture but anyone who is interested in finding out more about what makes Steve Reich tick. It was certainly an education for me.
Steve Reich’s musical career started when he took piano lessons and then started studying the drums at the age of 14. This interview began with his move to San Francisco in 1962 where he decided to become a cabbie so that he wouldn’t have to teach. Emma asked whether it was hard to make music around his day job. “Night job” he corrected her. “Necessity is the mother of invention – I coulda taught harmony and theory in Nebraska but I’d had it up to here with the academic world.” He saw how his friends became beaten down. “In my time almost all the composers in the US were in universities because that was the easiest job to get but I’m sure that now even being a DJ will be turned into academic trash. But you need to put a lot of energy into teaching and I think if you can’t then that’s immoral, and if you do then you’re gonna be too wiped out to make music.” Surely a sage piece of advice to anyone considering juggling teaching with a successful artistic career. “I had a good time driving the cab and I wasn’t invested in it – it really fit me and was making more money than most musical professors too!”
Unfortunately he wasn’t a cab driver for long: “I inched forward and bumped into someone and ended up working in a post office.” Emma asked if this was an influential period – down amongst the sounds of the ‘street’. “I don’t know how true that would be. All music comes from a time and place. I come from New York, the West Coast, during the 1960s and 70s.” New York was a noisy place to be. “I used to wander around with earplugs in.” He attributes his early experimentations with loops and phasing on a tape machine to such ideas being “in the air” during that period. “You are who you are and your music will bear evidence to the honesty of the situation.”
In the early 60s the Cuban Missile Crisis got everyone “kinda concerned… we felt the clock was ticking. The crisis passed but it made its mark.” In 1964 he recorded Brother Walter in Union Square preaching about the flood and created seminal work “It’s Gonna Rain” where he used the sounds without focusing on their meaning. “Do you hear the ‘wap wap’ in the background? That’s the wings of a pigeon, a pigeon drummer.” He described at length how he played around with the sounds, feeding them through mono into stereo and then back again, to offset the source material and create the pioneering phasing technique that has influenced many contemporary composers since. Because he cut the tape loops by hand there was always going to be a bit of drift, creating a “sense of direction”. He gleefully describes how the sound “slides across your testicles, it’s really creepy! You can feel the vibration, and then it gets to one ear sooner than the other.” He found it intriguing that he could splice things together to make sounds that resembled the beats found in African music. “I thought – what have I got here? Mechanised Africans!” The piece becomes progressively more spooky and paranoid in feel. “We’re in the ark, locking the door, it’s the end of the world… a betrayal in sound.” Lest we doubt this sudden moribund turn he confirms, “Yes, I was in a bad state of mind at the time and given what was going on in the world.”
A trip to Ghana in 1971 to study music was a key turning point. “All music there was a religiously, politically or historically orientated part of everyday life.” Whilst there he managed to contract malaria by picking up 100s of bites on his sandalled feet, despite a dose of anti-malarials. He realised that music was a form of communication that families were morally obliged to upkeep, but laughed that he met a Ghanaian man many years later who was no longer interested in “grandpa’s music”. Tastes change all over the world.
But Steve was keen not to fall into the trap of trying to adopt African music wholesale. “Many people from my generation drowned in India – it’s like an ocean containing thousands of years of music and as an individual it’s hard to make any sense out of it.” He bought some gang gangs in Ghana – iron bells that are used to accompany songs with a beautiful rattle. “They’re not that big, and I bought six of them. I thought I would use them in my music, but I don’t have perfect pitch and I was like ‘what do I do? They don’t sound right, should I get out the metal file?’ But then I felt like they would be saying ‘hi, I’m a gang gang, pleased to meet you,’ if I used them in my music. I am not an African and they carry the weight of a culture that’s not mine – so I had to think about what I had learnt that could travel, and that was the structure.”
He returned keen to play around with rhythmical complexity of the kind that is used in jazz such as the big band classic Africa/Brass by Coltrane. “It sounds like elephants coming through the jungle for half an hour, there’s no harmonic movement and yet it’s definitely not boring!” He concluded that there is tension and intensity precisely because there is no change. “In Shotgun by Junior Walker you’re waiting for another section, but there is no other section. There was something in the air [during that period] and it was harmonic stasis – even Bob Dylan was experimenting with one chord. It was coming in from other sources outside the west; the structural idea of a canon is an empty vessel that can travel anywhere.”
1971 was also the last year that Steve used the looped tape phasing technique, although he was keen not to be rude about laptop music in a room full of predominantly electronic musicians. “My live ideas came from a machine because all divisions are permeable.” Yet he felt trapped by gadgetry. “I felt like ‘I can’t leave this thing and I can’t do it live!’ I didn’t want to be a little tape maker.” The fact remains that he sees synthesisers and their ilk primarily as a means to an end. “I like the analogue sound so I was excited when the sampler was invented.” He felt liberated and exhilarated once he was able to say “look ma, no tape!” and started teaching ensembles to play his compositions live without the aid of traditional musical notation. Since then he has always toured with a close clique of musicians that he’s worked with for many years. “We’re the gold standard but other generations have picked it up. For instance the musicians in Riga in Latvia burnt Music for 18 Musicians right down into the ground.” Nowadays he uses midi mockups of live compositions to send out to performers and his musical style has become increasingly complex.

Steve Reich & Emma Warren in conversation by Gemma Milly.
Emma asked if there was some benefit in musicians learning his compositions without the benefit of written musical scores. “When music began we can speculate that there was no notation. Even early notation is in question. Notation as we know it started during the 10th and 11th centuries in the West – to save music for posterity. There were little pockets where people wrote things down, such as some isolated forms in Indonesia, but it was a marginal thing.” He concluded that notated music has only ever formed a very small part of all the music created worldwide and wonders if it even has a future. “Nowadays the normal position for walking down the street is like this,” he says, standing, head down, arm up, as if his mobile is in his hand. “It won’t be without it’s consequences…”
Steve believes that folk music can be used to describe whatever we interact with that’s around us, and can spontaneously arise in any culture. “Pop music is the folk music of our culture so in some sense electronics are the folk instrument of our time.” We’d come to the end of the guided lecture time, and sat in awed silence as Steve Reich played arguably his most famous piece, Music for 18 Musicians, through the huge lecture PA system. That is until an abrupt technical glitch snapped us all out of our reverie. “Anyone know how this thing works?!” asked Steve, frustratedly betraying his technophobery.
Find out how Steve answered a series of very well thought out questions from the floor in the next blog…

Steve Reich by Gemma Milly.
Steve Reich is a seriously cult figure for contemporary beats based music. Famed for his minimalist compositions from the 60s onwards he continues to be active today and even though I’ve heard he can be a difficult old bugger to interview at 74 years of age he was charming and lucid when he gave his lecture for the students of the 2010 Red Bull Music Academy.

Red Bull Music Academy lecture theatre.
I skirted into the back of the packed lecture theatre just as he was starting – and I use the term ‘lecture theatre’ lightly because we are talking the most comfortable lecture theatre you ever saw. Designer arm chairs stuffed with colour co-ordinated cushions were orientated around a sofa interview area above which hung the distinctive Red Bull coat of arms, for sale if you will. Emma “rabbit” Warren, who I’ve known since I was an intern at The Face over a decade ago, was tasked with asking the questions because over the years she has carved a niche for herself in this particular music scene and has found herself a “team member” of the academy.

Emma Warren by Gemma Milly.
What follows is by no means a direct transcription of the interview, but an edited version that I hope will make sense to not only those who attended the lecture but anyone who is interested in finding out more about what makes Steve Reich tick. It was certainly an education for me.
Steve Reich’s musical career started when he took piano lessons and then started studying the drums at the age of 14. This interview began with his move to San Francisco in 1962 where he decided to become a cabbie so that he wouldn’t have to teach. Emma asked whether it was hard to make music around his day job. “Night job” he corrected her. “Necessity is the mother of invention – I coulda taught harmony and theory in Nebraska but I’d had it up to here with the academic world.” He saw how his friends became beaten down. “In my time almost all the composers in the US were in universities because that was the easiest job to get but I’m sure that now even being a DJ will be turned into academic trash. But you need to put a lot of energy into teaching and I think if you can’t then that’s immoral, and if you do then you’re gonna be too wiped out to make music.” Surely a sage piece of advice to anyone considering juggling teaching with a successful artistic career. “I had a good time driving the cab and I wasn’t invested in it – it really fit me and was making more money than most musical professors too!”
Unfortunately he wasn’t a cab driver for long: “I inched forward and bumped into someone and ended up working in a post office.” Emma asked if this was an influential period – down amongst the sounds of the ‘street’. “I don’t know how true that would be. All music comes from a time and place. I come from New York, the West Coast, during the 1960s and 70s.” New York was a noisy place to be. “I used to wander around with earplugs in.” He attributes his early experimentations with loops and phasing on a tape machine to such ideas being “in the air” during that period. “You are who you are and your music will bear evidence to the honesty of the situation.”
In the early 60s the Cuban Missile Crisis got everyone “kinda concerned… we felt the clock was ticking. The crisis passed but it made its mark.” In 1964 he recorded Brother Walter in Union Square preaching about the flood and created seminal work “It’s Gonna Rain” where he used the sounds without focusing on their meaning. “Do you hear the ‘wap wap’ in the background? That’s the wings of a pigeon, a pigeon drummer.” He described at length how he played around with the sounds, feeding them through mono into stereo and then back again, to offset the source material and create the pioneering phasing technique that has influenced many contemporary composers since. Because he cut the tape loops by hand there was always going to be a bit of drift, creating a “sense of direction”. He gleefully describes how the sound “slides across your testicles, it’s really creepy! You can feel the vibration, and then it gets to one ear sooner than the other.” He found it intriguing that he could splice things together to make sounds that resembled the beats found in African music. “I thought – what have I got here? Mechanised Africans!” The piece becomes progressively more spooky and paranoid in feel. “We’re in the ark, locking the door, it’s the end of the world… a betrayal in sound.” Lest we doubt this sudden moribund turn he confirms, “Yes, I was in a bad state of mind at the time and given what was going on in the world.”
A trip to Ghana in 1971 to study music was a key turning point. “All music there was a religiously, politically or historically orientated part of everyday life.” Whilst there he managed to contract malaria by picking up 100s of bites on his sandalled feet, despite a dose of anti-malarials. He realised that music was a form of communication that families were morally obliged to upkeep, but laughed that he met a Ghanaian man many years later who was no longer interested in “grandpa’s music”. Tastes change all over the world.
But Steve was keen not to fall into the trap of trying to adopt African music wholesale. “Many people from my generation drowned in India – it’s like an ocean containing thousands of years of music and as an individual it’s hard to make any sense out of it.” He bought some gang gangs in Ghana – iron bells that are used to accompany songs with a beautiful rattle. “They’re not that big, and I bought six of them. I thought I would use them in my music, but I don’t have perfect pitch and I was like ‘what do I do? They don’t sound right, should I get out the metal file?’ But then I felt like they would be saying ‘hi, I’m a gang gang, pleased to meet you,’ if I used them in my music. I am not an African and they carry the weight of a culture that’s not mine – so I had to think about what I had learnt that could travel, and that was the structure.”
He returned keen to play around with rhythmical complexity of the kind that is used in jazz such as the big band classic Africa/Brass by Coltrane. “It sounds like elephants coming through the jungle for half an hour, there’s no harmonic movement and yet it’s definitely not boring!” He concluded that there is tension and intensity precisely because there is no change. “In Shotgun by Junior Walker you’re waiting for another section, but there is no other section. There was something in the air [during that period] and it was harmonic stasis – even Bob Dylan was experimenting with one chord. It was coming in from other sources outside the west; the structural idea of a canon is an empty vessel that can travel anywhere.”
1971 was also the last year that Steve used the looped tape phasing technique, although he was keen not to be rude about laptop music in a room full of predominantly electronic musicians. “My live ideas came from a machine because all divisions are permeable.” Yet he felt trapped by gadgetry. “I felt like ‘I can’t leave this thing and I can’t do it live!’ I didn’t want to be a little tape maker.” The fact remains that he sees synthesisers and their ilk primarily as a means to an end. “I like the analogue sound so I was excited when the sampler was invented.” He felt liberated and exhilarated once he was able to say “look ma, no tape!” and started teaching ensembles to play his compositions live without the aid of traditional musical notation. Since then he has always toured with a close clique of musicians that he’s worked with for many years. “We’re the gold standard but other generations have picked it up. For instance the musicians in Riga in Latvia burnt Music for 18 Musicians right down into the ground.” Nowadays he uses midi mockups of live compositions to send out to performers and his musical style has become increasingly complex.

Steve Reich & Emma Warren in conversation by Gemma Milly.
Emma asked if there was some benefit in musicians learning his compositions without the benefit of written musical scores. “When music began we can speculate that there was no notation. Even early notation is in question. Notation as we know it started during the 10th and 11th centuries in the West – to save music for posterity. There were little pockets where people wrote things down, such as some isolated forms in Indonesia, but it was a marginal thing.” He concluded that notated music has only ever formed a very small part of all the music created worldwide and wonders if it even has a future. “Nowadays the normal position for walking down the street is like this,” he says, standing, head down, arm up, as if his mobile is in his hand. “It won’t be without it’s consequences…”
Steve believes that folk music can be used to describe whatever we interact with that’s around us, and can spontaneously arise in any culture. “Pop music is the folk music of our culture so in some sense electronics are the folk instrument of our time.” We’d come to the end of the guided lecture time, and sat in awed silence as Steve Reich played arguably his most famous piece, Music for 18 Musicians, through the huge lecture PA system. That is until an abrupt technical glitch snapped us all out of our reverie. “Anyone know how this thing works?!” asked Steve, frustratedly betraying his technophobery.
Find out how Steve answered a series of very well thought out questions from the floor in the next blog…

Steve Reich by Gemma Milly.
Steve Reich is a seriously cult figure for contemporary beats based music. Famed for his minimalist compositions from the 60s onwards he continues to be active today and even though I’ve heard he can be a difficult old bugger to interview at 74 years of age he was charming and lucid when he gave his lecture for the students of the 2010 Red Bull Music Academy.

Red Bull Music Academy lecture theatre.
I skirted into the back of the packed lecture theatre just as he was starting – and I use the term ‘lecture theatre’ lightly because we are talking the most comfortable lecture theatre you ever saw. Designer arm chairs stuffed with colour co-ordinated cushions were orientated around a sofa interview area above which hung the distinctive Red Bull coat of arms, page if you will. Emma “rabbit” Warren, who I’ve known since I was an intern at The Face over a decade ago, was tasked with asking the questions because over the years she has carved a niche for herself in this particular music scene and has found herself a “team member” of the academy.

Emma Warren by Gemma Milly.
What follows is by no means a direct transcription of the interview, but an edited version that I hope will make sense to not only those who attended the lecture but anyone who is interested in finding out more about what makes Steve Reich tick. It was certainly an education for me.
Steve Reich’s musical career started when he took piano lessons and then started studying the drums at the age of 14. This interview began with his move to San Francisco in 1962 where he decided to become a cabbie so that he wouldn’t have to teach. Emma asked whether it was hard to make music around his day job. “Night job” he corrected her. “Necessity is the mother of invention – I coulda taught harmony and theory in Nebraska but I’d had it up to here with the academic world.” He saw how his friends became beaten down. “In my time almost all the composers in the US were in universities because that was the easiest job to get but I’m sure that now even being a DJ will be turned into academic trash. But you need to put a lot of energy into teaching and I think if you can’t then that’s immoral, and if you do then you’re gonna be too wiped out to make music.” Surely a sage piece of advice to anyone considering juggling teaching with a successful artistic career. “I had a good time driving the cab and I wasn’t invested in it – it really fit me and was making more money than most musical professors too!”
Unfortunately he wasn’t a cab driver for long: “I inched forward and bumped into someone and ended up working in a post office.” Emma asked if this was an influential period – down amongst the sounds of the ‘street’. “I don’t know how true that would be. All music comes from a time and place. I come from New York, the West Coast, during the 1960s and 70s.” New York was a noisy place to be. “I used to wander around with earplugs in.” He attributes his early experimentations with loops and phasing on a tape machine to such ideas being “in the air” during that period. “You are who you are and your music will bear evidence to the honesty of the situation.”
In the early 60s the Cuban Missile Crisis got everyone “kinda concerned… we felt the clock was ticking. The crisis passed but it made its mark.” In 1964 he recorded Brother Walter in Union Square preaching about the flood and created seminal work “It’s Gonna Rain” where he used the sounds without focusing on their meaning. “Do you hear the ‘wap wap’ in the background? That’s the wings of a pigeon, a pigeon drummer.” He described at length how he played around with the sounds, feeding them through mono into stereo and then back again, to offset the source material and create the pioneering phasing technique that has influenced many contemporary composers since. Because he cut the tape loops by hand there was always going to be a bit of drift, creating a “sense of direction”. He gleefully describes how the sound “slides across your testicles, it’s really creepy! You can feel the vibration, and then it gets to one ear sooner than the other.” He found it intriguing that he could splice things together to make sounds that resembled the beats found in African music. “I thought – what have I got here? Mechanised Africans!” The piece becomes progressively more spooky and paranoid in feel. “We’re in the ark, locking the door, it’s the end of the world… a betrayal in sound.” Lest we doubt this sudden moribund turn he confirms, “Yes, I was in a bad state of mind at the time and given what was going on in the world.”

Steve Reich & Emma Warren in conversation by Gemma Milly.
A trip to Ghana in 1971 to study music was a key turning point. “All music there was a religiously, politically or historically orientated part of everyday life.” Whilst there he managed to contract malaria by picking up 100s of bites on his sandalled feet, despite a dose of anti-malarials. He realised that music was a form of communication that families were morally obliged to upkeep, but laughed that he met a Ghanaian man many years later who was no longer interested in “grandpa’s music”. Tastes change all over the world.
But Steve was keen not to fall into the trap of trying to adopt African music wholesale. “Many people from my generation drowned in India – it’s like an ocean containing thousands of years of music and as an individual it’s hard to make any sense out of it.” He bought some gang gangs in Ghana – iron bells that are used to accompany songs with a beautiful rattle. “They’re not that big, and I bought six of them. I thought I would use them in my music, but I don’t have perfect pitch and I was like ‘what do I do? They don’t sound right, should I get out the metal file?’ But then I felt like they would be saying ‘hi, I’m a gang gang, pleased to meet you,’ if I used them in my music. I am not an African and they carry the weight of a culture that’s not mine – so I had to think about what I had learnt that could travel, and that was the structure.”
He returned keen to play around with rhythmical complexity of the kind that is used in jazz such as the big band classic Africa/Brass by Coltrane. “It sounds like elephants coming through the jungle for half an hour, there’s no harmonic movement and yet it’s definitely not boring!” He concluded that there is tension and intensity precisely because there is no change. “In Shotgun by Junior Walker you’re waiting for another section, but there is no other section. There was something in the air [during that period] and it was harmonic stasis – even Bob Dylan was experimenting with one chord. It was coming in from other sources outside the west; the structural idea of a canon is an empty vessel that can travel anywhere.”
1971 was also the last year that Steve used the looped tape phasing technique, although he was keen not to be rude about laptop music in a room full of predominantly electronic musicians. “My live ideas came from a machine because all divisions are permeable.” Yet he felt trapped by gadgetry. “I felt like ‘I can’t leave this thing and I can’t do it live!’ I didn’t want to be a little tape maker.” The fact remains that he sees synthesisers and their ilk primarily as a means to an end. “I like the analogue sound so I was excited when the sampler was invented.” He felt liberated and exhilarated once he was able to say “look ma, no tape!” and started teaching ensembles to play his compositions live without the aid of traditional musical notation. Since then he has always toured with a close clique of musicians that he’s worked with for many years. “We’re the gold standard but other generations have picked it up. For instance the musicians in Riga in Latvia burnt Music for 18 Musicians right down into the ground.” Nowadays he uses midi mockups of live compositions to send out to performers and his musical style has become increasingly complex.
Emma asked if there was some benefit in musicians learning his compositions without the benefit of written musical scores. “When music began we can speculate that there was no notation. Even early notation is in question. Notation as we know it started during the 10th and 11th centuries in the West – to save music for posterity. There were little pockets where people wrote things down, such as some isolated forms in Indonesia, but it was a marginal thing.” He concluded that notated music has only ever formed a very small part of all the music created worldwide and wonders if it even has a future. “Nowadays the normal position for walking down the street is like this,” he says, standing, head down, arm up, as if his mobile is in his hand. “It won’t be without it’s consequences…”
Steve believes that folk music can be used to describe whatever we interact with that’s around us, and can spontaneously arise in any culture. “Pop music is the folk music of our culture so in some sense electronics are the folk instrument of our time.” We’d come to the end of the guided lecture time, and sat in awed silence as Steve Reich played arguably his most famous piece, Music for 18 Musicians, through the huge lecture PA system. That is until an abrupt technical glitch snapped us all out of our reverie. “Anyone know how this thing works?!” asked Steve, frustratedly betraying his technophobery.
Find out how Steve answered a series of very well thought out questions from the floor in the next blog…

Steve Reich by Gemma Milly.
Steve Reich is a seriously cult figure for contemporary beats based music. Famed for his minimalist compositions from the 60s onwards he continues to be active today and even though I’ve heard he can be a difficult old bugger to interview, cheap at 74 years of age he was charming and lucid when he gave his lecture to the students of the 2010 Red Bull Music Academy.

Red Bull Music Academy lecture theatre.
I skirted into the back of the packed lecture theatre just as he was starting – and I use the term ‘lecture theatre’ lightly because we are talking the most comfortable lecture theatre you ever saw. Designer arm chairs stuffed with colour co-ordinated cushions were orientated around a sofa interview area above which hung the distinctive Red Bull coat of arms, if you will. Emma “rabbit” Warren, who I’ve known since I was an intern at The Face over a decade ago, was tasked with asking the questions – over the years she has carved a niche for herself in this particular music scene and acts as a “team member” for the academy.

Emma Warren by Gemma Milly.
What follows is by no means a direct transcription of the interview, but an edited version that I hope will make sense to not only those who attended the lecture but anyone who is interested in finding out more about what makes Steve Reich tick. It was certainly an education for me.
Steve Reich‘s musical career started with piano lessons and then the study of drums at the age of 14. This conversation began with his move to San Francisco in 1962 where he decided to become a cabbie so that he wouldn’t have to teach. Emma asked whether it was hard to make music around his day job. “Night job,” he corrected her. “Necessity is the mother of invention – I coulda taught harmony and theory in Nebraska but I’d had it up to here with the academic world.” He saw how his friends became beaten down. “In my time almost all the composers in the US were in universities because that was the easiest job to get but I’m sure that now even being a DJ will be turned into academic trash. But you need to put a lot of energy into teaching and I think if you can’t then that’s immoral, and if you do then you’re gonna be too wiped out to make music.” Surely a sage piece of advice to anyone considering juggling teaching with a successful artistic career. “I had a good time driving the cab and I wasn’t invested in it – it really fit me and was making more money than most musical professors too!”
Unfortunately he wasn’t a cab driver for long: “I inched forward and bumped into someone and ended up working in a post office.” Emma asked if this was an influential period – down amongst the sounds of the ‘street’. “I don’t know how true that would be. All music comes from a time and place. I come from New York, the West Coast, during the 1960s and 70s.” New York was a noisy place to be. “I used to wander around with earplugs in.” He attributes his early experimentations with loops and phasing on a tape machine to such ideas being “in the air” during that period. “You are who you are and your music will bear evidence to the honesty of the situation.”
In the early 60s the Cuban Missile Crisis got everyone “kinda concerned… we felt the clock was ticking. The crisis passed but it made its mark.” In 1964 he recorded Brother Walter in Union Square preaching about the flood and created seminal work “It’s Gonna Rain” where he made use of the sounds without focusing on their meaning. “Do you hear the ‘wap wap’ in the background? That’s the wings of a pigeon, a pigeon drummer.” He described at length how he played around with the sounds, feeding them through mono into stereo and then back again, to offset the source material and create the pioneering phasing technique that has influenced many contemporary composers since. Because he cut the tape loops by hand there was always going to be a bit of drift, creating a “sense of direction”. He gleefully describes how the sound “slides across your testicles, it’s really creepy! You can feel the vibration, and then it gets to one ear sooner than the other.” He found it intriguing that he could splice things together to make sounds that resembled the beats found in African music. “I thought – what have I got here? Mechanised Africans!” The piece becomes progressively more spooky and paranoid in feel. “We’re in the ark, locking the door, it’s the end of the world… a betrayal in sound.” Lest we doubt this sudden moribund turn he confirms, “Yes, I was in a bad state of mind at the time and given what was going on in the world.”

Steve Reich & Emma Warren in conversation by Gemma Milly.
A trip to Ghana in 1971 to study music was a key turning point. “All music there was a religiously, politically or historically orientated part of everyday life.” Whilst there he managed to contract malaria by picking up 100s of bites on his sandalled feet, despite a dose of anti-malarials. He realised that music was a form of communication that families were morally obliged to upkeep, but laughed that he met a Ghanaian man many years later who was no longer interested in “grandpa’s music”. Tastes change all over the world.
But Steve was keen not to fall into the trap of trying to adopt African music wholesale. “Many people from my generation drowned in India – it’s like an ocean containing thousands of years of music and as an individual it’s hard to make any sense out of it.” He bought some gang gangs in Ghana – iron bells that are used to accompany songs with a beautiful rattle. “They’re not that big, and I bought six of them. I thought I would use them in my music, but I don’t have perfect pitch and I was like ‘what do I do? They don’t sound right, should I get out the metal file?’ But then I felt like they would be saying ‘hi, I’m a gang gang, pleased to meet you,’ if I used them in my music. I am not an African and they carry the weight of a culture that’s not mine – so I had to think about what I had learnt that could travel, and that was the structure.”
He returned keen to play around with rhythmical complexity of the kind that is used in jazz such as the big band classic Africa/Brass by Coltrane. “It sounds like elephants coming through the jungle for half an hour, there’s no harmonic movement and yet it’s definitely not boring!” He concluded that there was tension and intensity precisely because there was no change. “In Shotgun by Junior Walker you’re waiting for another section, but there is no other section. There was something in the air [during that period] and it was harmonic stasis – even Bob Dylan was experimenting with one chord. It was coming in from other sources outside the west; the structural idea of a canon as an empty vessel that can travel anywhere.”
1971 was also the last year that Steve used the looped tape phasing technique, although he was keen not to be rude about laptop music in a room full of predominantly electronic musicians. “My live ideas came from a machine because all divisions are permeable.” Yet he felt trapped by gadgetry. “I felt like ‘I can’t leave this thing and I can’t do it live!’ I didn’t want to be a little tape maker.” The fact remains that he sees synthesisers and their ilk primarily as a means to an end. “I like the analogue sound so I was excited when the sampler was invented.” He felt liberated and exhilarated once he was able to say “look ma, no tape!” and started teaching ensembles to play his compositions live without the aid of traditional musical notation. Since then his music has got progressively more complex and he has always toured with a close clique of live musicians that he’s worked with for many years. “We’re the gold standard but other generations have picked it up. For instance the musicians in Riga in Latvia burnt Music for 18 Musicians right down into the ground.” Nowadays he uses midi mockups of live compositions to send out for performers to learn across the world.
Emma asked if there was some benefit in musicians learning his compositions without the benefit of written musical scores. “When music began we can speculate that there was no notation. Even early notation is in question. Notation as we know it started during the 10th and 11th centuries in the West – to save music for posterity. There were little pockets where people wrote things down, such as some isolated forms in Indonesia, but it was a marginal thing.” He concluded that notated music has only ever formed a very small part of all the music created worldwide and wonders if it even has a future. “Nowadays the normal position for walking down the street is like this,” he says, standing, head down, arm up, as if his mobile is in his hand. “It won’t be without it’s consequences…”
Steve believes that folk music can be used to describe whatever we interact with that’s around us, and can spontaneously arise in any culture. “Pop music is the folk music of our culture so in some sense electronics are the folk instrument of our time.” We’d come to the end of the guided lecture time, and sat in awed silence as Steve Reich played arguably his most famous piece, Music for 18 Musicians, through the huge lecture PA system… that is until an abrupt technical glitch snapped us all out of our reverie. “Anyone know how this thing works?!” asked Steve, frustratedly betraying his technophobery.
Find out how Steve answered a series of very well thought out questions from the floor in the next blog…

Steve Reich by Gemma Milly.
Steve Reich is a seriously cult figure for contemporary beats based music. Famed for his minimalist compositions from the 60s onwards he continues to be active today and even though I’ve heard he can be a difficult old bugger to interview, this site at 74 years of age he was charming and lucid when he gave his lecture to the students of the 2010 Red Bull Music Academy.

Red Bull Music Academy lecture theatre.
I skirted into the back of the packed lecture theatre just as he was starting – and I use the term ‘lecture theatre’ lightly because we are talking the most comfortable lecture theatre you ever saw. Designer arm chairs stuffed with colour co-ordinated cushions were orientated around a sofa interview area above which hung the distinctive Red Bull coat of arms, stomach if you will. Emma “rabbit” Warren, who I’ve known since I was an intern at The Face over a decade ago, was tasked with asking the questions – over the years she has carved a niche for herself in this particular music scene and acts as a “team member” for the academy.

Emma Warren by Gemma Milly.
What follows is by no means a direct transcription of the interview, but an edited version that I hope will make sense to not only those who attended the lecture but anyone who is interested in finding out more about what makes Steve Reich tick. It was certainly an education for me.
Steve Reich‘s musical career started with piano lessons and then the study of drums at the age of 14. This conversation began with his move to San Francisco in 1962 where he decided to become a cabbie so that he wouldn’t have to teach. Emma asked whether it was hard to make music around his day job. “Night job,” he corrected her. “Necessity is the mother of invention – I coulda taught harmony and theory in Nebraska but I’d had it up to here with the academic world.” He saw how his friends became beaten down. “In my time almost all the composers in the US were in universities because that was the easiest job to get but I’m sure that now even being a DJ will be turned into academic trash. But you need to put a lot of energy into teaching and I think if you can’t then that’s immoral, and if you do then you’re gonna be too wiped out to make music.” Surely a sage piece of advice to anyone considering juggling teaching with a successful artistic career. “I had a good time driving the cab and I wasn’t invested in it – it really fit me and was making more money than most musical professors too!”
Unfortunately he wasn’t a cab driver for long: “I inched forward and bumped into someone and ended up working in a post office.” Emma asked if this was an influential period – down amongst the sounds of the ‘street’. “I don’t know how true that would be. All music comes from a time and place. I come from New York, the West Coast, during the 1960s and 70s.” New York was a noisy place to be. “I used to wander around with earplugs in.” He attributes his early experimentations with loops and phasing on a tape machine to such ideas being “in the air” during that period. “You are who you are and your music will bear evidence to the honesty of the situation.”
In the early 60s the Cuban Missile Crisis got everyone “kinda concerned… we felt the clock was ticking. The crisis passed but it made its mark.” In 1964 he recorded Brother Walter in Union Square preaching about the flood and created seminal work “It’s Gonna Rain” where he made use of the sounds without focusing on their meaning. “Do you hear the ‘wap wap’ in the background? That’s the wings of a pigeon, a pigeon drummer.” He described at length how he played around with the sounds, feeding them through mono into stereo and then back again, to offset the source material and create the pioneering phasing technique that has influenced many contemporary composers since. Because he cut the tape loops by hand there was always going to be a bit of drift, creating a “sense of direction”. He gleefully describes how the sound “slides across your testicles, it’s really creepy! You can feel the vibration, and then it gets to one ear sooner than the other.” He found it intriguing that he could splice things together to make sounds that resembled the beats found in African music. “I thought – what have I got here? Mechanised Africans!” The piece becomes progressively more spooky and paranoid in feel. “We’re in the ark, locking the door, it’s the end of the world… a betrayal in sound.” Lest we doubt this sudden moribund turn he confirms, “Yes, I was in a bad state of mind at the time and given what was going on in the world.”

Steve Reich & Emma Warren in conversation by Gemma Milly.
A trip to Ghana in 1971 to study music was a key turning point. “All music there was a religiously, politically or historically orientated part of everyday life.” Whilst there he managed to contract malaria by picking up 100s of bites on his sandalled feet, despite a dose of anti-malarials. He realised that music was a form of communication that families were morally obliged to upkeep, but laughed that he met a Ghanaian man many years later who was no longer interested in “grandpa’s music”. Tastes change all over the world.
But Steve was keen not to fall into the trap of trying to adopt African music wholesale. “Many people from my generation drowned in India – it’s like an ocean containing thousands of years of music and as an individual it’s hard to make any sense out of it.” He bought some gang gangs in Ghana – iron bells that are used to accompany songs with a beautiful rattle. “They’re not that big, and I bought six of them. I thought I would use them in my music, but I don’t have perfect pitch and I was like ‘what do I do? They don’t sound right, should I get out the metal file?’ But then I felt like they would be saying ‘hi, I’m a gang gang, pleased to meet you,’ if I used them in my music. I am not an African and they carry the weight of a culture that’s not mine – so I had to think about what I had learnt that could travel, and that was the structure.”
He returned keen to play around with rhythmical complexity of the kind that is used in jazz such as the big band classic Africa/Brass by Coltrane. “It sounds like elephants coming through the jungle for half an hour, there’s no harmonic movement and yet it’s definitely not boring!” He concluded that there was tension and intensity precisely because there was no change. “In Shotgun by Junior Walker you’re waiting for another section, but there is no other section. There was something in the air [during that period] and it was harmonic stasis – even Bob Dylan was experimenting with one chord. It was coming in from other sources outside the west; the structural idea of a canon as an empty vessel that can travel anywhere.”
1971 was also the last year that Steve used the looped tape phasing technique, although he was keen not to be rude about laptop music in a room full of predominantly electronic musicians. “My live ideas came from a machine because all divisions are permeable.” Yet he felt trapped by gadgetry. “I felt like ‘I can’t leave this thing and I can’t do it live!’ I didn’t want to be a little tape maker.” The fact remains that he sees synthesisers and their ilk primarily as a means to an end. “I like the analogue sound so I was excited when the sampler was invented.” He felt liberated and exhilarated once he was able to say “look ma, no tape!” and started teaching ensembles to play his compositions live without the aid of traditional musical notation. Since then his music has got progressively more complex and he has always toured with a close clique of live musicians that he’s worked with for many years. “We’re the gold standard but other generations have picked it up. For instance the musicians in Riga in Latvia burnt Music for 18 Musicians right down into the ground.” Nowadays he uses midi mockups of live compositions to send out for performers to learn across the world.
Emma asked if there was some benefit in musicians learning his compositions without the benefit of written musical scores. “When music began we can speculate that there was no notation. Even early notation is in question. Notation as we know it started during the 10th and 11th centuries in the West – to save music for posterity. There were little pockets where people wrote things down, such as some isolated forms in Indonesia, but it was a marginal thing.” He concluded that notated music has only ever formed a very small part of all the music created worldwide and wonders if it even has a future. “Nowadays the normal position for walking down the street is like this,” he says, standing, head down, arm up, as if his mobile is in his hand. “It won’t be without it’s consequences…”
Steve believes that folk music can be used to describe whatever we interact with that’s around us, and can spontaneously arise in any culture. “Pop music is the folk music of our culture so in some sense electronics are the folk instrument of our time.” We’d come to the end of the guided lecture time, and sat in awed silence as Steve Reich played arguably his most famous piece, Music for 18 Musicians, through the huge lecture PA system… that is until an abrupt technical glitch snapped us all out of our reverie. “Anyone know how this thing works?!” asked Steve, frustratedly betraying his technophobery.
Find out how Steve answered a series of very well thought out questions from the floor in the next blog…

The designer interior of the Red Bull Music Academy by Gemma Milly.
Since the Red Bull Music Academy rolled into town just over a month ago I have been pursued by their PR to blog about the whole shebang. Unfortunately timings could not have been worse and whilst I have been concentrating on London Fashion Week the great and good of the electronic music world have been gathering in force to take part in this most singular of events. It therefore seems strangely fitting that I should finally publish my edit of the Steve Reich lecture that I attended on Tuesday 16th February on the very same day that it finally finishes.
If you live in London you cannot have escaped the presence of the Red Bull Music Academy, recipe mainly in the form of their lovingly produced daily newspaper, case the Daily Note, which has been handed out at tube and train stations across London with the same zeal as the Evening Standard every single day since it started. I absolutely cannot begin to imagine how much it must have cost to assemble the staff to put together such a fast turnaround daily paper, let alone pay the folk that stand around in the street to hand it out.

Inside a recording studio in the Red Bull Music Academy. I’ve got that G-Plan coffee table in my living room. Cost a tenner at a car boot sale.
All interior photos courtesy of Red Bull.
The amount spent on producing the Daily Note must pale into insignificance when compared with how much money has been poured into the actual Red Bull Music Academy itself – which is a mammoth venture that rolls into a different country every year. This isn’t just a fancy name for a bunch of club nights that the general public can attend (though it is that too), but does exactly what it says on the tin and is an actual academy where actual students can learn from the maestros of electronic music. Sixty carefully selected students from across the world have been whisked into central London, where they’ve been given free accommodation and food for the duration of their stay. At the academy, which is located in the Red Bull headquarters a stone’s throw from the London Dungeon in Bermondsey, they are treated to an amazing roster of talks and tutorials laid on by eminent musicians, producers, DJs and composers, all apparently giving their time for free to further the education of this talented bunch. The emphasis is on electronic and urban music, and on genres which are not usually championed by the establishment, so most of the names featured in the bulging programme will not be familiar to anyone but the geekiest music bod within that particular musical subcategory.


The amount of effort, let alone the money, that has been put into this venture is literally staggering. In the designer-decorated headquarters the skeletal office staff have been shunted into the top floors and the bottom few have been converted into something that would not look out of place on a reality show – featuring trendy young things lounging on plush sofas next to speccy music impresarios, a sparkling free cafe, pristine recording suites and buzzing glass walled rooms full of earnest Red Bull Music Academy staff. It is hard to fathom why such a big brand would so entirely align themselves with such a niche sub genre of music, but then this has got to be the most epic “anti-marketing” campaign I’ve ever known. Because no matter how lovingly those Daily Notes are put together I can’t believe many are actually more than skim read by some knackered commuter, and the vast majority will no doubt have been tossed straight into the bin by the mass public who just doesn’t care about this event or the music it champions. Will the Red Bull Music Academy, the busy events schedule or the Daily Note increase sales of Red Bull? Who knows, but for those lucky enough to be taking part as academy students it is surely a life changing opportunity.

bRUNA creating live music with a laptop.
It has to be said that the vast catalogue of acts involved aren’t really my cup of tea – I veer somewhat more on the indie side of life – but I decided to go along to the Sonar Pt 1 taster at the Roundhouse on Friday 5th March, where I then struggled to find something suited to my decidedly more indie/dance tastes. Upstairs what I heard as boos for the headline act were actually calls for hip hop legend Doom. DOOM! Downstairs I discovered something much more to my liking in the form of Red Bull Academy graduate bRUNA, a former lawyer from Spain. Unfortunately he wasn’t exactly what the earnest hip-hop heads had came for and the small room soon emptied. When I stayed on with my male partner bRUNA’s concerned girlfriend came over to check whether we really were there because we liked bRUNA’s cute Euro electro (we did). Or I should say: she came over and checked in with Tim. How funny that sexism should rear it’s ugly head in such a setting. Such was my ire that I did say to her pointedly – actually it’s me you want to be talking to.
I have only recently been inducted into the wonders of Steve Reich, but the event that looked most up my street was a lecture by this influential composer. And so it was that I found myself in the lecture theatre of the Red Bull Music Academy on a very rainy Tuesday afternoon. Read on to find out what Steve Reich revealed to his students…
After Steve Reich had completed his conversation with Emma Warren there were a series of thought provoking questions from the Red Bull Music Academy students:
How do you balance the listenability of your music with what you want to create?
When I write I’m alone in the music, shop and my theory is if I love it I hope you do too, find but I think it’s valid to question listenability if you’re writing a jingle. It’s not the same with a fine art composition. People are intuitively smart about music so you can’t fool them – they will smell a rat [if your music doesn’t come from the heart]
How easy is it to get into composition if you’re not classically trained?
Sometimes you can see shapes in music and follow them. My son got Pro tools and everything changed because he suddenly saw what he was doing and the eye got involved in addition to the ear. It changes your perspective when you can see the music you are composing. I work with Sibelius; it’s easy to learn the basics but you should ask yourself – will it be useful? Will it help you?
Are you interested in audio illusions?
Well I haven’t used phasing since the 70s but [having said that] my entire arsenal of equipment is macbook pro, cheapest sibelius and Reason. My new piece will feature speech samples from 9/11and they are triggered from a notation programme. I also wanted to create the equivalent in sound of stop action in a film, and something called granular synthesis can stop a sound anywhere, even on a consonant. – I saw a fishhhhhhhh….. it does a fantastic job of it.
Of course the audience want to know more about his new project…
During 9/11 I was living on Broadway, four blocks from Ground Zero. My son and grandkids were in the apartment when it happened, and I won’t go into details but it was terrifying but basically our neighbours saved my family. I didn’t do anything about it but a year ago I realised I had unfinished business and so I’m in the middle of a new piece based on the Jewish tradition whereby you don’t leave a body before it’s buried. These women didn’t know what parts were in the tents [at Ground Zero] but they came down and said psalms 24 hours a day.
I worry that I’m saying something flippant now, but how did you describe your music in the early days?
Hey, lighten up, they got London once so let’s hope they’re not back in a hurry!
It’s not important what you call your music: journalists want a label, but they’ll invent something anyway so it doesn’t matter. Philip Glass calls it repetitive music. I didn’t like minimal but it’s better than trance or some other things. If a journalist ever pushes you on this say ‘wash out your mouth, it’s your job to write the next piece’. Don’t put yourself in a box – it’s someone else’s job to do that. Be polite though, and don’t make enemies if you don’t have to.
What is the process when you start writing? And how much has it changed?
Oh boy! I briefly did pieces for orchestra, and they were by far not my best works; they were too phat. I learnt that in the late 80s, so since the beginning, minus a little break, I have written for ensemble, e.g. six pianos. I want identical pairs of instruments. Before Music for 18 Musicians I used rhythmic melodic pattern, like drumming on a phone but then I thought what happens if if I worked things out harmonically and it really worked, so I continued. I start with a harmonic super structure, which before computers was done on a multi track tape. I’ve always worked in real sound, not in my head. I’m a crippled man, I have to hear it! In the mid 80s I got a grant and bought a Tascam 8 track, which weighed a tonne, but I used it for the next ten years until midi appeared. Different Trains was composed on a mac plus which was easy. No, that’s a complete lie, it crashed every 15 seconds! I invent harmonic movements that don’t come intuitively, which is a bit like hanging onto a horse for dear life [to keep control] All the details are done on computer but there is a lot of garbage. My trash can runneth over!
How do you advise moving from the creation of songs to symphonies or longer works?
It’s usually a mess when pop musicians try to do that – for example I would never advise Radiohead to write a symphony – they’re geniuses anyway so why bother. Anyone who doesn’t recognise that is mad. But if you are really serious about it it may mean going to music school to get the practical knowledge, which could be a laborious series of years.
Do you think it’s better to concentrate on emotion or concept?
Bach was the greatest improviser of his day but I’m not much of one so the bedrock of anything I’ve ever done has rested on musical intuition. How does it sound on Monday, Tuesday, next month? Does it keep sounding good?
And with that there is a standing ovation for this most revered of modern composers. I think there’s a room full of people here who will go away and reappraise the ouvre of Steve Reich if they haven’t already done so.
After Steve Reich had completed his conversation with Emma Warren there were a series of thought provoking questions from the Red Bull Music Academy students:
How do you balance the listenability of your music with what you want to create?
When I write I’m alone in the music, sickness and my theory is if I love it I hope you do too, viagra but I think it’s valid to question listenability if you’re writing a jingle. It’s not the same with a fine art composition. People are intuitively smart about music so you can’t fool them – they will smell a rat [if your music doesn’t come from the heart]
How easy is it to get into composition if you’re not classically trained?
Sometimes you can see shapes in music and follow them. My son got Pro tools and everything changed because he suddenly saw what he was doing and the eye got involved in addition to the ear. It changes your perspective when you can see the music you are composing. I work with Sibelius; it’s easy to learn the basics but you should ask yourself – will it be useful? Will it help you?
Are you interested in audio illusions?
Well I haven’t used phasing since the 70s but [having said that] my entire arsenal of equipment is macbook pro, visit this site sibelius and Reason. My new piece will feature speech samples from 9/11and they are triggered from a notation programme. I also wanted to create the equivalent in sound of stop action in a film, and something called granular synthesis can stop a sound anywhere, even on a consonant. – I saw a fishhhhhhhh….. it does a fantastic job of it.
Of course the audience want to know more about his new project…
During 9/11 I was living on Broadway, four blocks from Ground Zero. My son and grandkids were in the apartment when it happened, and I won’t go into details but it was terrifying but basically our neighbours saved my family. I didn’t do anything about it but a year ago I realised I had unfinished business and so I’m in the middle of a new piece based on the Jewish tradition whereby you don’t leave a body before it’s buried. These women didn’t know what parts were in the tents [at Ground Zero] but they came down and said psalms 24 hours a day.
I worry that I’m saying something flippant now, but how did you describe your music in the early days?
Hey, lighten up, they got London once so let’s hope they’re not back in a hurry!
It’s not important what you call your music: journalists want a label, but they’ll invent something anyway so it doesn’t matter. Philip Glass calls it repetitive music. I didn’t like minimal but it’s better than trance or some other things. If a journalist ever pushes you on this say ‘wash out your mouth, it’s your job to write the next piece’. Don’t put yourself in a box – it’s someone else’s job to do that. Be polite though, and don’t make enemies if you don’t have to.
What is the process when you start writing? And how much has it changed?
Oh boy! I briefly did pieces for orchestra, and they were by far not my best works; they were too phat. I learnt that in the late 80s, so since the beginning, minus a little break, I have written for ensemble, e.g. six pianos. I want identical pairs of instruments. Before Music for 18 Musicians I used rhythmic melodic pattern, like drumming on a phone but then I thought what happens if if I worked things out harmonically and it really worked, so I continued. I start with a harmonic super structure, which before computers was done on a multi track tape. I’ve always worked in real sound, not in my head. I’m a crippled man, I have to hear it! In the mid 80s I got a grant and bought a Tascam 8 track, which weighed a tonne, but I used it for the next ten years until midi appeared. Different Trains was composed on a mac plus which was easy. No, that’s a complete lie, it crashed every 15 seconds! I invent harmonic movements that don’t come intuitively, which is a bit like hanging onto a horse for dear life [to keep control] All the details are done on computer but there is a lot of garbage. My trash can runneth over!
How do you advise moving from the creation of songs to symphonies or longer works?
It’s usually a mess when pop musicians try to do that – for example I would never advise Radiohead to write a symphony – they’re geniuses anyway so why bother. Anyone who doesn’t recognise that is mad. But if you are really serious about it it may mean going to music school to get the practical knowledge, which could be a laborious series of years.
Do you think it’s better to concentrate on emotion or concept?
Bach was the greatest improviser of his day but I’m not much of one so the bedrock of anything I’ve ever done has rested on musical intuition. How does it sound on Monday, Tuesday, next month? Does it keep sounding good?
And with that there is a standing ovation for this most revered of modern composers. I think there’s a room full of people here who will go away and reappraise the ouvre of Steve Reich if they haven’t already done so.

The Tiny by Rosalie Hoskins.
When I slipped the new album Gravity & Grace by The Tiny into my desktop, look I had no expectations. I’d never heard of this self-released Swedish phenomenon, cialis 40mg and I doubt that many of my British readers will have either. But I hope all that is set to change, because their third album is a stunning collection of songs from a couple who wear their hearts in their voices and melodies. When I heard that Leo and Ellekari would be playing in London I made it my business to get along and have a short chat with them.
Leo and Ellekari met in 2002, fell in love, moved into a house together and six months later started a band. It doesn’t get more idyllic than this surely? Well yes it does, despite setbacks and the temporary dissolution of the band a few years ago (it was relationship/band make or break time) the pair recently got married, reformed the band with renewed vigour, and are expecting their first child this summer. Why takes things by halves eh?
Both of them come from long musical backgrounds. Leo went to the Royal Danish Academy of Music in Copenhagen for a year before realising that he wasn’t quite cut out to play in a symphony orchestra and transferring to the Academy of Music in Gothenburg, where he could “make up my own education.” He may wield his cello with all the finesse of a classically trained musician but he insists that “it’s all bluffing really.” Ellekari (which is a Sammi name) learnt all sorts of brass instruments when she was younger and did stints as a jazz singer during her teens in her father’s big band before moving on to a series of punk and ska outfits. They both play bits of glockenspiel, synth, organ and piano as well. Between them they’ve worked extensively with some of the best contemporary Scandinavian musicians, including The Concretes, Peter Bjorn & John, Jenny Wilson, and Ane Brun. In the UK they’ve toured with the likes of Camera Obscura and Ed Harcourt.

The Tiny at the Union Chapel. Photography by Amelia Gregory.
I wanted to know what inspired their name and Ellekari tells me that she wanted it to sound the opposite of all those bands that say “we’re the greatest, the best… and it might fool people into thinking we’re pop.” Their first album, Close Enough “which doesn’t refer to our relationship but rather the fact that it took only two days to record” was released in 2004, followed by Starring Someone Like You in 2006 – both far sparser and less lush that their latest offering, all pared down cello and bare vocals. I don’t think anyone could mistake them for a pop band, although the jazz influence is clear. Leo confirms that this stripped down aesthetic affected their choice of name. “When we first started our music was very deconstructed and there was a lot of silence.” Ellekari has a distinctive quavering voice which at times sounds a bit like that other great warbling songstress, Joanna Newsom – whose vocals I happen to find highly grating. Not so with Ellekari’s offering, who has a far wider range and is capable of much stronger emotion and reach.
Much mileage is made out of The Tiny‘s relationship in their songwriting and in latest single Last Weekend Ellekari clambers on top of a grand piano in a forest to bemoan the lack of commitment in their life. She wears an over the top wedding dress with huge feathered eyelashes whilst Leo saws at his cello in a tail coat and white boxer shorts, eyes blackened. “I could not stand to looooooose you” she opines. Soon they are both hacking the wedding banquet and piano to pieces and one can only imagine the conversations that happened behind the scenes before, during and after this song was made. For this couple at least it seems as though working out their relationship dilemmas through music has resulted in a happy ending, for they got married just as this video was released.
Since the beginning The Tiny have released all their own records with very little money behind them. “it’s always been very hard and lots of work, but no one else wants to do it!” says Leo, “but it has given us the freedom to do whatever we want to do whenever we like.” Most of their friends on major labels complain just as much “so I suppose there are always problems whichever side you are on,” says Ellekari. “It’s a nice way of life but of course we can’t do everything on our own, for instance we have no idea where to start in England!” They didn’t really have a plan to release Gravity & Grace in the UK but when they started to get booking agency requests they decided to go with the “tailwind”. They’re already popular in France so decided to release the album in conjunction with their French collaborator Almost Musique and UK mega distributor Cargo.

The Tiny at the Union Chapel. Photography by Amelia Gregory.
Do they think that the sudden rise in their popularity can be ascribed to the reach of the internet? “Definitely!” says Leo, who thinks that sites like Spotify and Myspace have been integral in spreading music, although he doesn’t really see the point of twitter. “We don’t twitter about what we eat. I don’t really know how to use it, I’m too old.” Rubbish! You can follow and encourage them here. I should have told him that the main demographic on twitter is 30-50 year olds. Because their other albums have gradually trickled out over the years their online presence has grown organically. “It feels as if we have grown into a new position with this album – and it definitely feels easier this time around.”
I wonder if having a baby has slightly thrown their plans to promote the new record (this is the first time their UK PR has heard the news). “Not really because we never plan too far ahead anyway. Music is spreading in a different way and in different time stretches,” says Ellekari. “We don’t feel we have to follow a set plan because we want to make music for the rest of our lives.” She does joke that her mum is already booked in to look after the baby, though it might be a push to make any of the festivals this year. “We have no idea how it will work,” concedes Leo.
At the Union Chapel in Islington on March 4th 2010 they play with fellow Swedes First Aid Kit for the first time, although they sang together collaboratively with Anne Ternheim on Summer Rain last year and have nothing but the highest praise for these talented sisters many years younger than themselves. Is the Stockholm scene comforting or claustrophobic? “Well, most Swedes tour a lot outside Sweden because there is such a limited audience there.” They enjoy touring in France because it’s pleasurable to play in nice venues where people are really into their music. What about the food I say, always thinking of my stomach. “Yes, good food helps!”
With that we finish on the very important subject of what Ellekari will be wearing for the concert tonight. She’ll be leaving her fabulous zebra print t-shirt in the dressing room and instead donning a long glittery vintage dress from the 70s that she found in Hungary for “next to nothing.” There must be something in the air, for both First Aid Kit girls are wearing vintage maxi dresses too.

The Tiny: Gravity & Grace.
It is with sadness that I will now admit that I missed The Tiny’s Union Chapel concert, but I did make it back in time to see headliners First Aid Kit, which you can also read about here. I really do hope that The Tiny decide the UK is as much fun to tour as France, even with a small baby in tow.
Written by Amelia Gregory on Saturday March 13th, 2010 2:56 pm
Categories ,Almost Musique, ,Ane Brun, ,Anne Ternheim, ,Camera Obscura, ,cargo, ,copenhagen, ,Ed Harcourt, ,festivals, ,First Aid Kit, ,france, ,Gothenburg, ,Gravity & Grace, ,jazz, ,Jenny Wilson, ,joanna newsom, ,myspace, ,Peter Bjorn & John, ,Spotify, ,sweden, ,The Concretes, ,The Tiny, ,twitter, ,union chapel
Similar Posts: